List Of Vacuum Tube Computers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
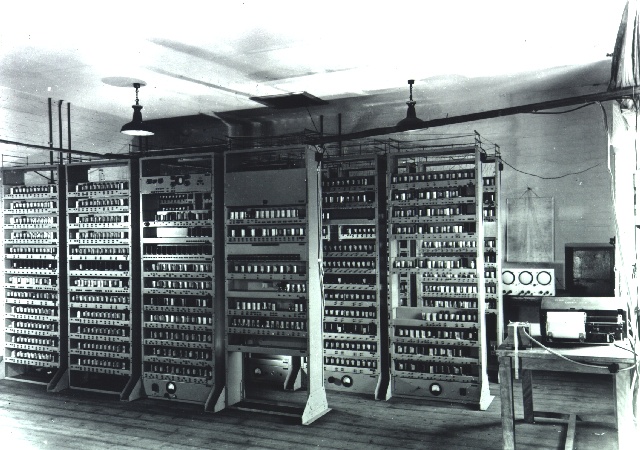 Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using
Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using
 Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using
Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using vacuum-tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as a ...
logic circuitry. They were preceded by systems using electromechanical relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
s and followed by systems built from discrete transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch e ...
s. Some later computers on the list had both vacuum tubes and transistors.
This list of vacuum-tube computers is sorted by date put into service:
}) are identical, except input-output equipment. Both were used internally.
, -
, The Wegematic 1000 , , 1960
, , , Improved version of the ALWAC III-E
The ALWAC III-E was an early commercial vacuum-tube computer employing a rotating magnetic drum main storage unit, operational in 1955. It weighed about .
The invention of the ALWAC III-E is attributed to Axel Wenner-Gren, and the name is derived ...
, -
, ZRA 1 , , 1960
, , , Built by VEB Carl Zeiss, Jena, German Democratic RepublicSiegmar Gerber: ''Einsatz von Zeiss-Rechnern für Forschung, Lehre und Dienstleistung in Informatik in der DDR – eine Bilanz''. GI-Edition, Bonn 2006, p. 310–318
, -
, Minsk-1
Minsk-1 Airport was a Belarusian airport located within the city limits of Minsk, just a few kilometres south from the centre.
History
Minsk-1 was built in 1933. It was the major airport of Minsk until the new airport ''Minsk-2'', now named ...
, , 1960
, , , Built in Minsk
, -
, Odra 1001 , , 1960
, , , First computer built by Elwro
Elwro was a Polish company that manufactured mainframe and microcomputers from 1959 until 1989. Its plant was in Wroclaw. Computer models included Odra mainframe systems, and the Elwro 800 Junior microcomputer for education.
Overview
The Wr ...
, Wroclaw, Poland
, -
, Minsk-1
Minsk-1 Airport was a Belarusian airport located within the city limits of Minsk, just a few kilometres south from the centre.
History
Minsk-1 was built in 1933. It was the major airport of Minsk until the new airport ''Minsk-2'', now named ...
, , 1960
, , , Built in Minsk
, -
, G3 , , 1961
, , , Built by the Max Planck Institute for Physics
The Max Planck Institute for Physics (MPP) is a physics institute in Munich, Germany that specializes in high energy physics and astroparticle physics. It is part of the Max-Planck-Gesellschaft and is also known as the Werner Heisenberg Institu ...
in Göttingen, esp. by Heinz Billing
Heinz Billing (7 April 1914 – 4 January 2017) was a German physicist and computer scientist, widely considered a pioneer in the construction of computer systems and computer data storage, who built a prototype laser interferometric gravitation ...
, -
, Sumlock ANITA calculator
The ANITA Mark VII and ANITA Mark VIII calculators were launched simultaneously in late 1961 as the world's first all-electronic desktop calculators. Designed and built by the Bell Punch Co. in Britain, and marketed through its Sumlock Compt ...
, , 1961
, <10,000/year, , Desktop calculator
, -
, UMC-1 , , 1962
, , , Developed in Poland, it used the unusual negabinary
A negative base (or negative radix) may be used to construct a non-standard positional numeral system. Like other place-value systems, each position holds multiples of the appropriate power of the system's base; but that base is negative—that is ...
number system internally
, -
, BRLESC
The BRLESC I (Ballistic Research Laboratories Electronic Scientific Computer) was one of the last of the first-generation electronic computers. It was built by the United States Army's Ballistic Research Laboratory (BRL) at Aberdeen Proving Gro ...
, , 1962
, 1, , 1,727 tubes and 853 transistors
, -
, OSAGE , , 1963
, 1, , Close copy of the Rice Institute Computer The Rice Institute Computer, also known as the Rice Computer or R1, was a 54-bit tagged architecture, section "II.", "PREVIOUS WORK" digital computer built during 1958–1961 (partially operational beginning in 1959) on the campus of Rice University ...
built at the University of Oklahoma
The University of Oklahoma (OU) is a Public university, public research university in Norman, Oklahoma. Founded in 1890, it had existed in Oklahoma Territory near Indian Territory for 17 years before the two Territories became the state of Oklahom ...
See also
*List of transistorized computers
This is a list of transistorized computers, which were digital computers that used discrete transistors as their primary logic elements. Discrete transistors were a feature of logic design for computers from about 1960, when reliable transistors ...
* History of computing hardware
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Vacuum Tube ComputersVacuum tube computers
Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using vacuum-tube logic circuitry. They were preceded by systems using electromechanical relays and followed by systems built from discrete transis ...
Computers, list of vacuum tube